Out Of This World Definition Of Speed In Physics

In physics however they do not have the same meaning and they are distinct concepts.
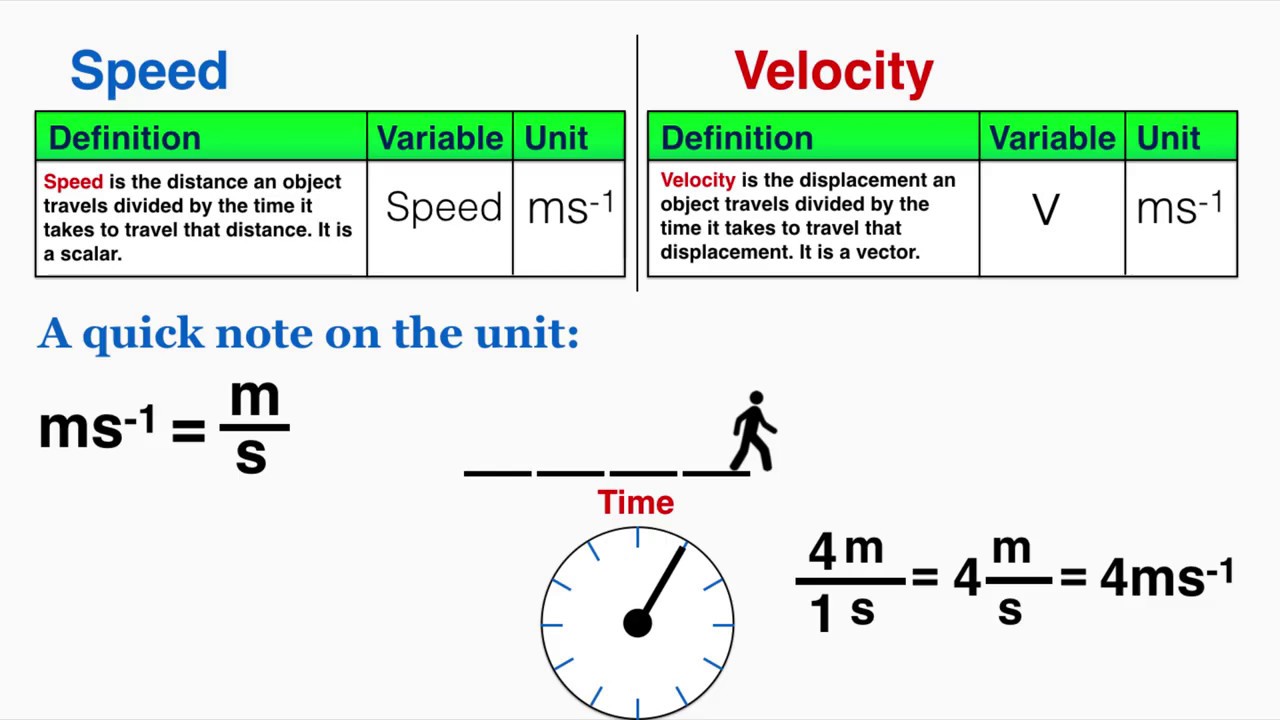
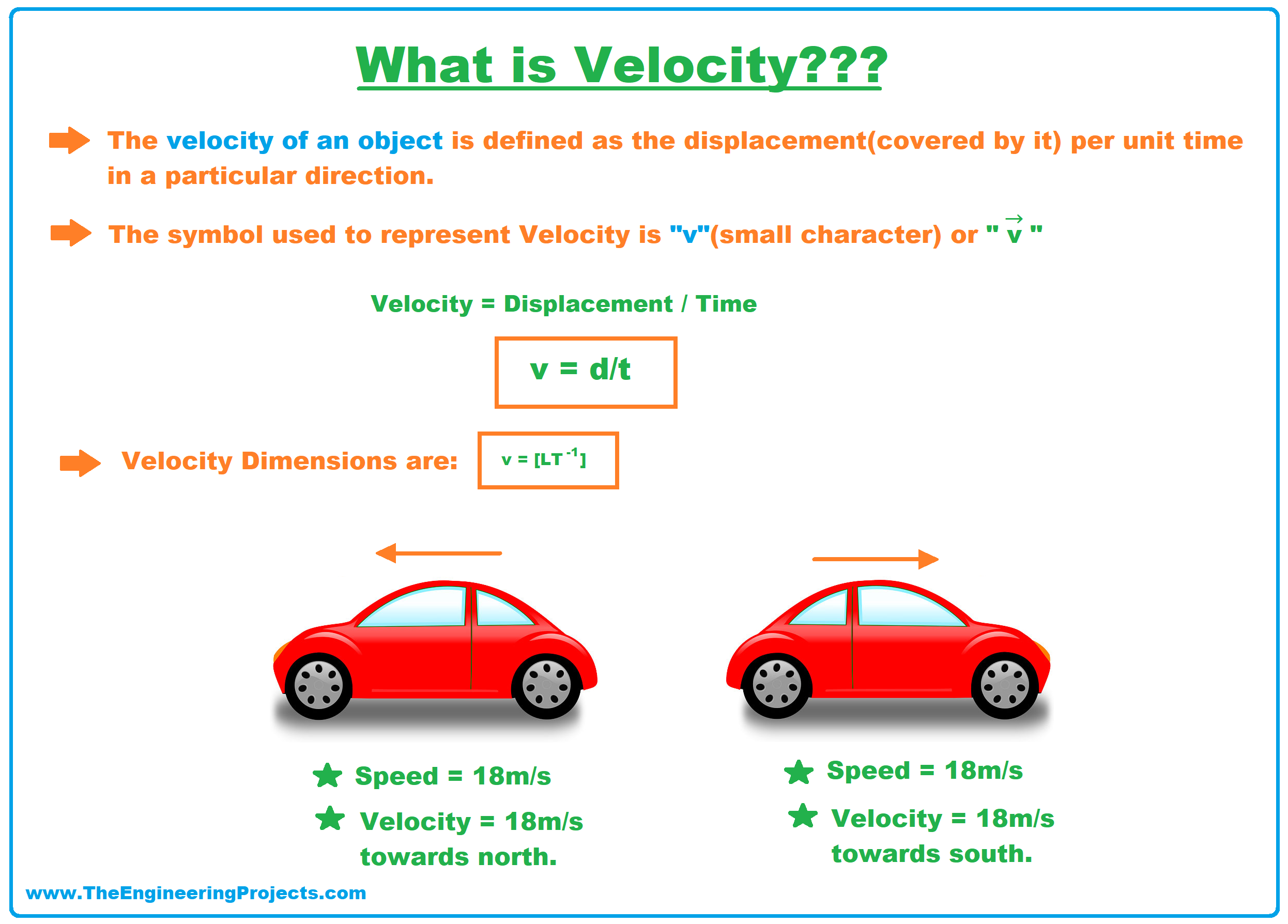
Definition of speed in physics. Lower speed means it is moving slower. The definition of Speed in Physics is the distance covered by an object in unit time. In everyday use and in kinematics the speed commonly referred to as v of an object is the magnitude of the rate of change of its position with time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time.
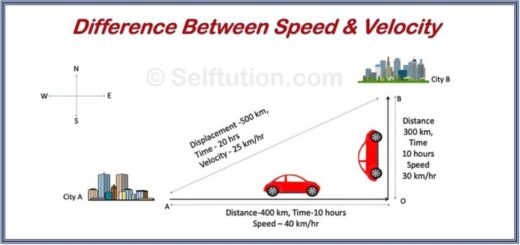
When something moves in a circular path at a constant speed and returns to its starting point its average velocity is zero but its average speed is found by dividing the circumference of the circle by the time taken to move around the circle. Put another way speed is a measure of distance traveled over a certain amount of time. In physics time describes change.
The arrow of time is defined by the thermodynamic concept of entropy. In science and physics the standard unit of measure for speed is generally meters per second or ms. In physics time is what clocks do.
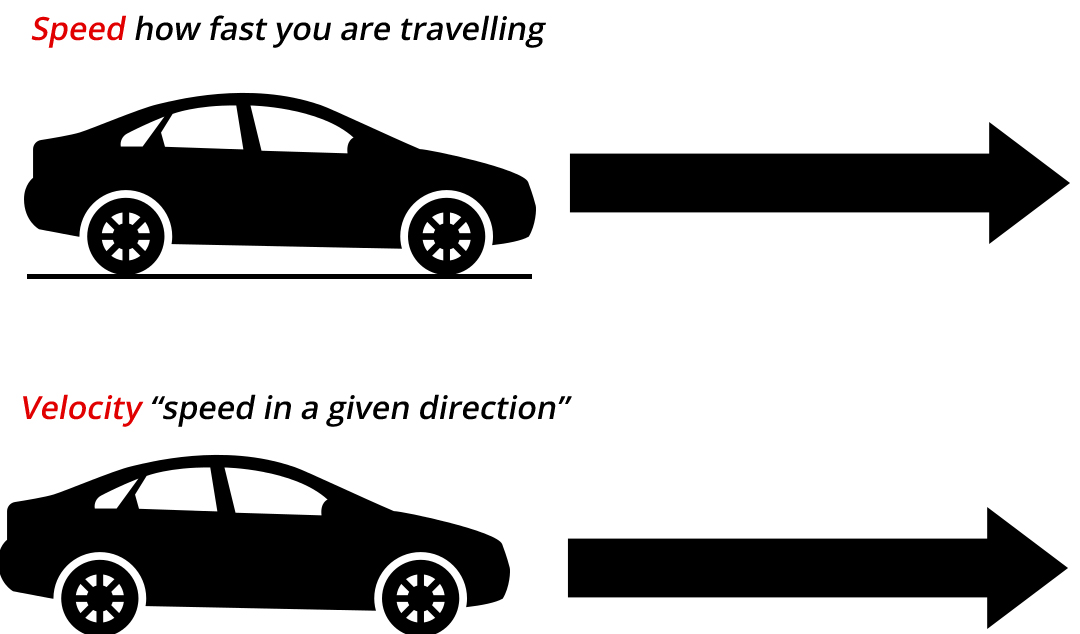
It tells us how fast or slow an object is moving. Speed is measured as the ratio of distance to the time in which the distance was covered. Speed is a scalar quantity so it has only magnitude not direction.
Speed is a scalar quantity as it has only direction and no magnitude. SPEED is defined as the distance traveled by the moving object in the unit time interval. Speed Formula in Physics Speed vfrac text Distance travelled s text Time taken t.
General Physics the constant maximum velocity reached by a body falling under gravity through a fluid esp the atmosphere 2. Speed is often described simply as the distance traveled per unit of. In other words the rate at which the object is moving is called speed.