Stunning Caramelization Reaction Mechanism

C hemistry behind the reaction Caramelization reactions take place under a.
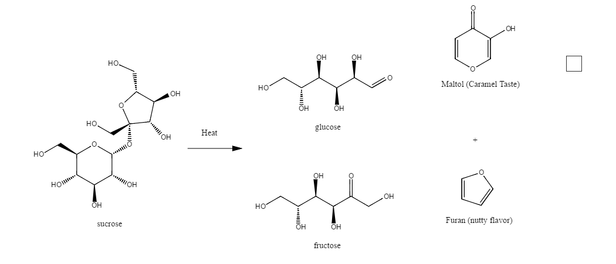
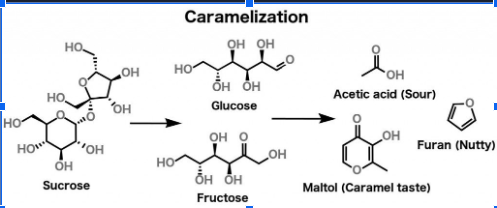
Caramelization reaction mechanism. The main reactions that occur during the heating process are the following. Caramels taste can be attributed to the different compounds produced within the caramelization reactions along with sweet sugars. Caramelization is a type of non-enzymatic browning reaction.
Caramelization of fructose which accounted for more than 40 of total UV-absorbance and 10 to 36 of brown color development may therefore lead to overestimating the Maillard reaction in foods. Nonenzymatic browning NEB reactions occur during the thermal processing and storage of foods. You could also say that its the oxidation of sugar or the degradation of sugars under heat.
Caramelization is a form of pyrolysis which is a generic term to denote any irreversible chemical decomposition driven by heat more specifically in the absence of oxygen. It is usually formed when sugars are being heated at high temperature above. Sugars are dehydrated and double bonds are introduced into the structures.
Caramelization is a type of non-enzymatic browning reaction of sugars which takes place under the action of dry heat and results in the formation of a characteristic caramel flavour. F46 Compare the two processes of non-enzymatic browning Maillard reaction and caramelization that cause the browning of food. Caramelization may sometimes cause browning in the same foods in which the Maillard reaction occurs but the two processes are distinct.
Caramelization refers to the browning of sugar. Lysine was moderately lost below pH 80. This is distinct from the maillard reaction in which amino acids and sugars react to form new compounds.
The mechanism of its formation is given in Fig. The process of caramelization starts with the melting of sugar at temperatures above 120 C. The result of heating sugars to these extreme temperatures is that they break down in a process known as pyrolysis.