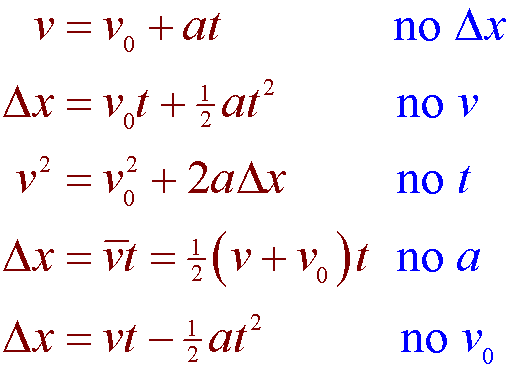Unique Acceleration Motion Equations

Here we will focus on motion in a straight line one dimension.
Acceleration motion equations. The equation reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. By definition acceleration is the first derivative of velocity with respect to time. Figure 318 illustrates this concept graphically.
Take the operation in that definition and reverse it. Consider a body moving in a straight line with uniform acceleration as shown in the figure. The kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be utilized to predict unknown information about an objects motion if other information is known.
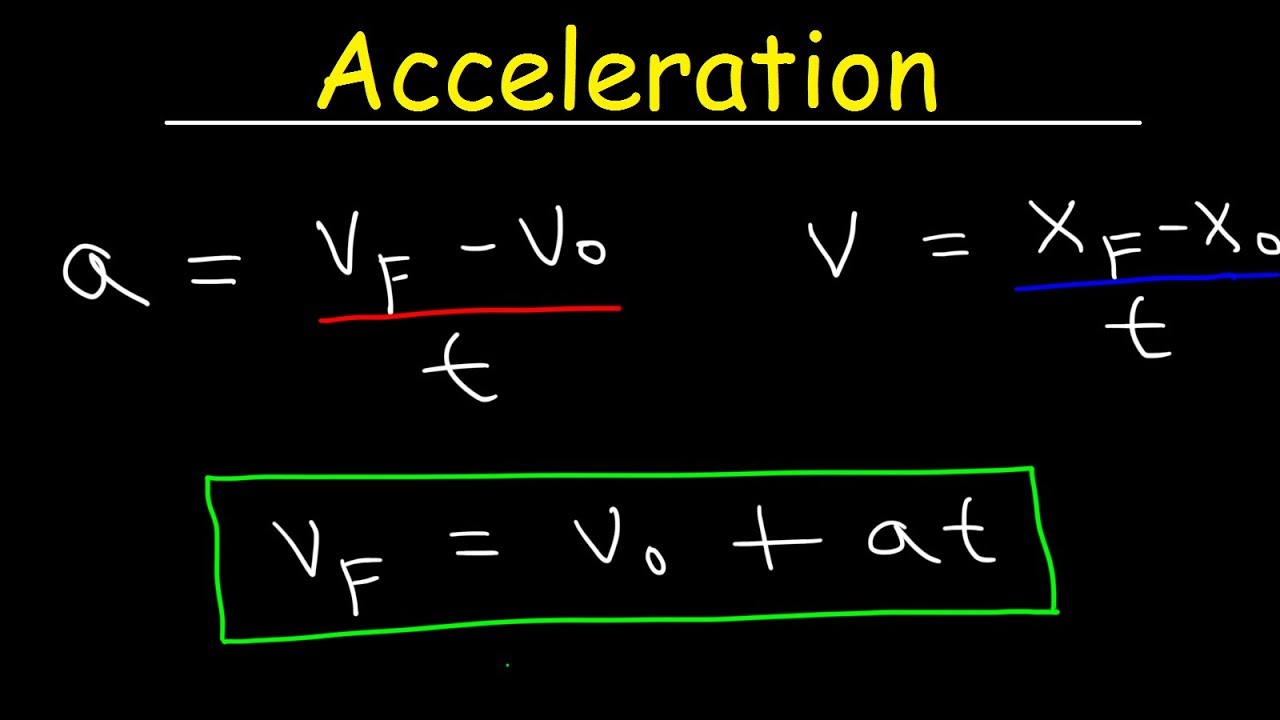
Equations of Motion Equations of motion relate the displacement of an object with its velocity acceleration and time. Its unit in the International System SI is the meter m v v0. Instead of differentiating velocity to find acceleration integrate acceleration to find velocity.
The equation v v0 v 2 reflects the fact that when acceleration is constant v is just the simple average of the initial and final velocities. Displacement s initial velocity u final velocity v acceleration a and time t. After all acceleration is one of the building blocks of physics.
Obtain equations of motion for constant acceleration using the method of calculus. There are three equations of motion that can be used to derive components such as displacement s velocity initial and final time t and acceleration. The average velocity is half way between the initial and final velocities.
Position of the body at a given time x and at the initial time x0. Initial velocity is less than its final velocity and then the acceleration is known as positive acceleration. Some other things to keep in mind when using the acceleration equation.